The cannabis plant contains active chemical compounds called cannabinoids, which are something of a miracle. In 1988, scientists discovered that the icy hairs containing resin glands, or trichomes, on cannabis leaves and flowers contain active chemical compounds (nearly ninety have been isolated so far) that plug into cannabinoid receptors in the human brain. These plant-based versions of chemicals that our brains produce when under stress is a carbon copy of the cannabinoids in human breast milk which will deliver powerful antioxidants and can shift neurological and physiological patterns.
The most famous, and nurtured, cannabinoid in cannabis is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC. THC triggers CB1 receptors, which are also mediated by anandamide, the first human cannabinoid discovered in 1992. CB1 receptors determine how we see, smell, listen, and feel hunger, pleasure, and pain – which is why everything is beautiful, food tastes and smells amazing, and reality television can be enjoyable when people consume cannabis.
THC also activates CB2 receptors in the liver, heart, kidneys, blood vessels, endocrine glands, and lymph cells, making it a good overall tonic, but its psychoactive element has made it the darling of cannabis users. Breeders have met consumer demand with sinsemilla increasing THC percentages in the high 20s and even into the 30s, though most cannabis today has less than 10 percent THC, according to the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws. A University in Mississippi’s notes that the average THC content has increased from 3 to 4 percent in the 1990s to 13 percent today. Specifics aside, most cannabis has more THC today than it did a decade or two ago.
Related Article: Recent Updates
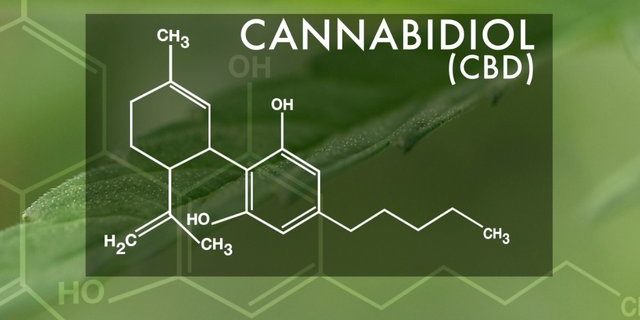
Cannabidiol (CBD) is an up-and-coming cannabinoid that’s getting high level attention because it delivers medical benefits without getting patients high. CBD, doesn’t bind to CB1 receptors, where psychoactive effects are triggered, and can actually mute THC’s psychoactive effects by opposing its actions at CB1 receptors. The CBD cannabinoid stimulates receptors that mediate pain, inflammation, and body temperature and regulate oxygen, blood, and dopamine. CBD slows down serotonin receptor signals, giving it an antidepressant effect. It’s being studied as a treatment for people with anxiety, sleep and eating disorders, and pain.
CBD was nearly bred out of most cannabis plants as growers sought more potently psychoactive cultivars over the past couple decades, and now researchers are scrambling to isolate the compound and study its medicinal effects. In 2013, a CNN documentary about Charlotte Figi, a young girl whose intractable seizures associated with Dravet syndrome were relieved after she ate oil made from a low THC, high CBD cultivar, spurred patients (and their parents) across the nation to seeking out CBDs. Breeders are meeting demand with cultivars containing up to 20 percent or more CBD content. Several states are considering or have passed legislation allowing patients to use CBD oil.
All Natural MD Florida issues medical marijuana doctor certifications and ID cards for patients suffering from one of the State approved Florida Medical Marijuana Registry Program qualifying conditions for a Florida medical marijuana card.

